Introduction of Inventory Control Systems
This content is summarized from the book: Silver, E. A., Pyke, D. F., & Thomas, D. J. (2016). Inventory and production management in supply chains. CRC press.
Every inventory control system in supply chain management is designed to resolve three fundamental problems under probabilistic demand:
- Review Frequency: How often should the inventory status be determined?
- Ordering Trigger: When should a replenishment order be placed?
- Order Size: How large should the replenishment order be?
1. Continuous Review and Periodic Review
The fundamental difference between the two methods is the review interval (R), defined as the time that elapses between two consecutive moments when the stock level is known.
Continuous Review: The stock status is always known because each transaction (shipment, receipt, demand) triggers an immediate update. This is often referred to as “transactions reporting”.
- Advantage: It requires less safety stock (SS) to provide the same level of customer service. Under continuous review, the inventory level can drop appreciably between reviews only during the lead time. In contrast, periodic systems must hold enough stock to cover demand for both the review interval and the lead time.
- Disadvantage: Order placement is irregular (whenever the reorder point is hit), making the workload on staff less predictable compared to a fixed schedule.
Periodic Review: The stock status is determined only every R units of time (e.g., weekly or daily). Between these moments, there is uncertainty regarding the inventory level.
- Advantage: It allows for the coordination of replenishments. For example, several items purchased from the same supplier or shipped via the same mode can be reviewed and ordered together. This consolidation can fill shipping containers efficiently and reduce costs. It allows for a reasonable prediction of staff workload, as orders are made at a rhythmic, regular pattern.
- Modern Context (POS Systems): Even when Point-of-Sale (POS) systems allow for continuous data collection, decisions are often still made periodically (e.g., at the end of the day) for convenience. In such cases, the review period is effectively R = 1 day.
2. Classification of items
Before selecting a policy, it is crucial to classify items based on their importance to the firm. Most firms segment items into three categories based on dollar sales volume:
- A Items (High Value): Typically make up 20% of the items but represent 80% of the dollar sales volume. These are critical to the business.
- B Items (Moderate Value): Comprise roughly 30% of the items and represent 15% of the dollar volume.
- C Items (Low Value): Comprise roughly 50% of the items but represent only 5% of the dollar volume.
Note: Firms often devote the most sophisticated control efforts to A items, simplified methods for B items, and manual/simple approaches for C items because the potential savings for C items are small.
3. Inventory Control Systems: The Four Policy Types
Overview & Definitions
Inventory control systems are defined by how often they check inventory (Review Interval) and how they determine the Order Size.
- s (Reorder Point): The inventory level that triggers a new order.
- Q (Order Quantity): A fixed amount ordered every time.
- S (Order-Up-To Level): The target maximum inventory level.
- R (Review Interval): The time between inventory checks.
Continuous Review Systems
Inventory is monitored constantly (effectively $R=0$). Orders are triggered immediately when stock drops to the reorder point.
A. Order-Point, Order-Quantity (s, Q)
- Mechanism: When inventory position \(\le s\), order a fixed quantity Q.
- Also Known As: The “Two-Bin System”.
- Best For: B Items (Moderate value/importance).
- Pros: Simple and predictable. Suppliers prefer it because the order size is always constant.
- Cons: Struggles with demand spikes. If a large order drops stock far below s, ordering just Q may not be enough to recover safely.
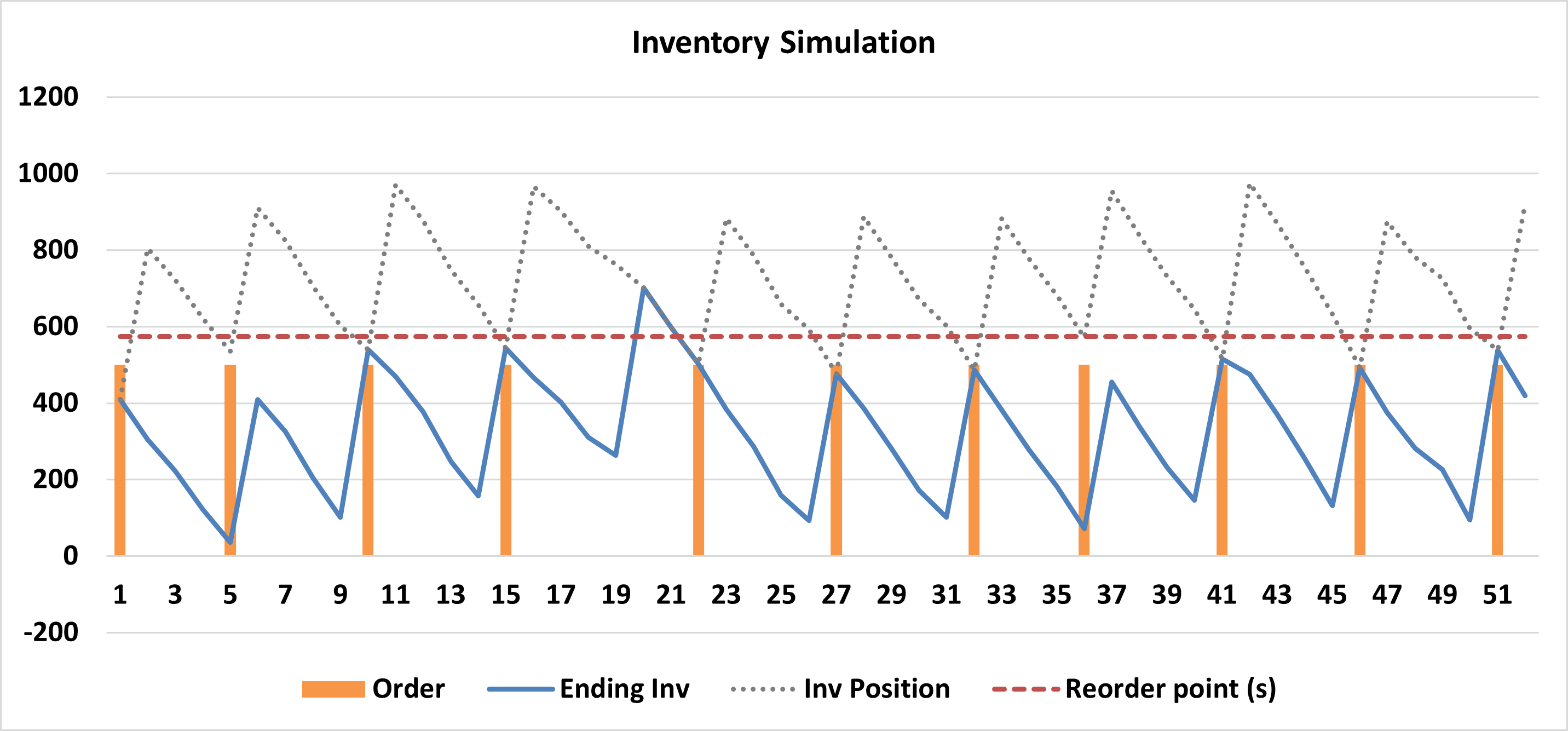
Example for (s,Q) policy.
B. Order-Point, Order-Up-to-Level (s, S)
- Mechanism: When inventory position \(\le s\), order enough to raise the level to S.
- Also Known As: The “Min-Max System”.
- Best For: A Items (High value/importance).
- Pros: robust against variable demand sizes. It guarantees inventory is restored to the full target level (S) regardless of how low it dropped.
- Cons: Mathematically complex to optimize compared to fixed-quantity systems.
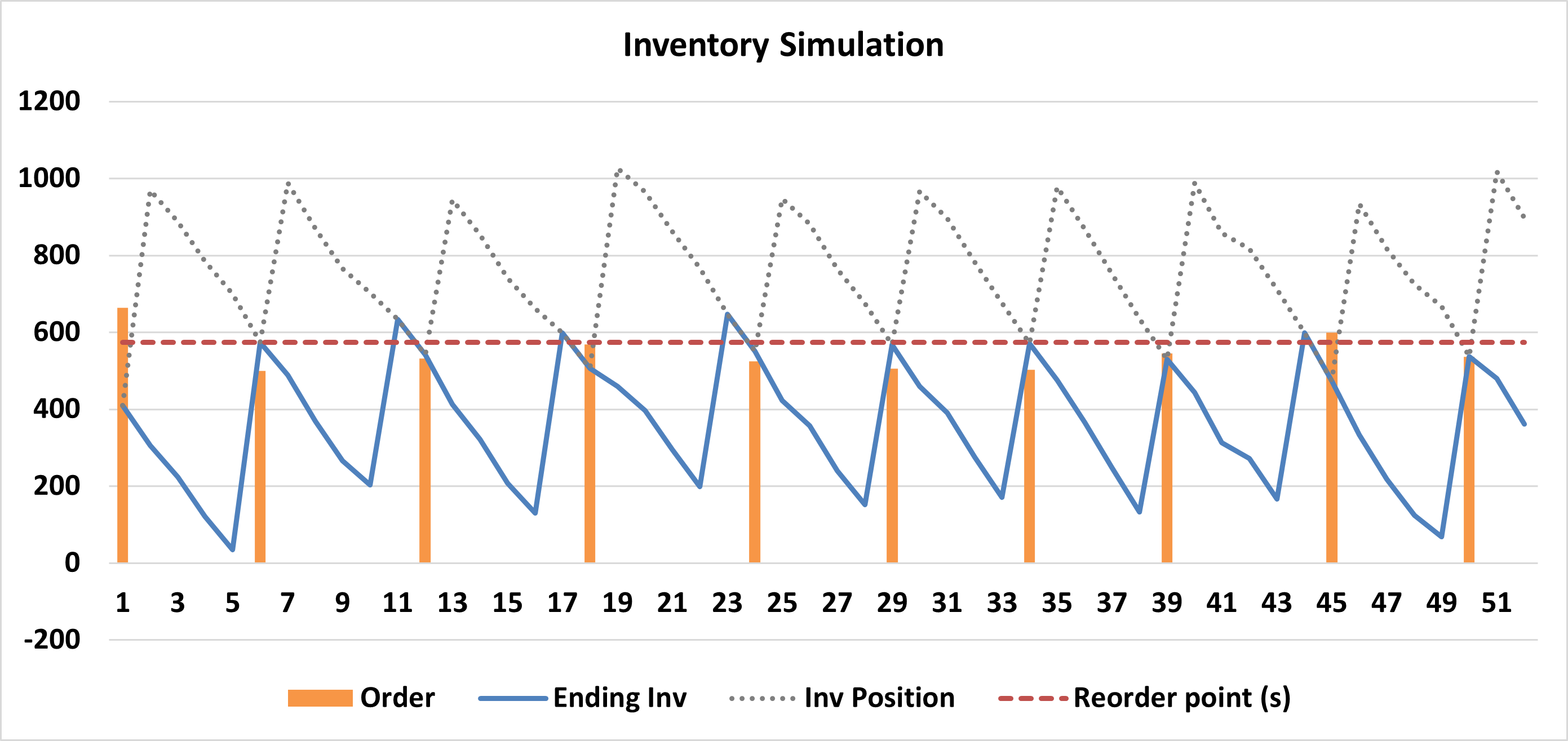
Example for (s,S) policy.
Periodic Review Systems
Inventory is checked only at fixed intervals (e.g., weekly or monthly). Between reviews, the system is “blind” to the stock level.
C. Periodic-Review, Order-Up-to-Level (R, S)
- Mechanism: Every R units of time, place an order to raise the inventory level to S.
- Also Known As: The “Replenishment Cycle System”.
- Best For: B Items (Moderate value/importance).
- Pros: Excellent for coordination. You can group orders for multiple items from one supplier to save on shipping costs.
- Cons: Requires higher safety stock/carrying costs because inventory must cover demand for the review interval (R) plus the lead time.
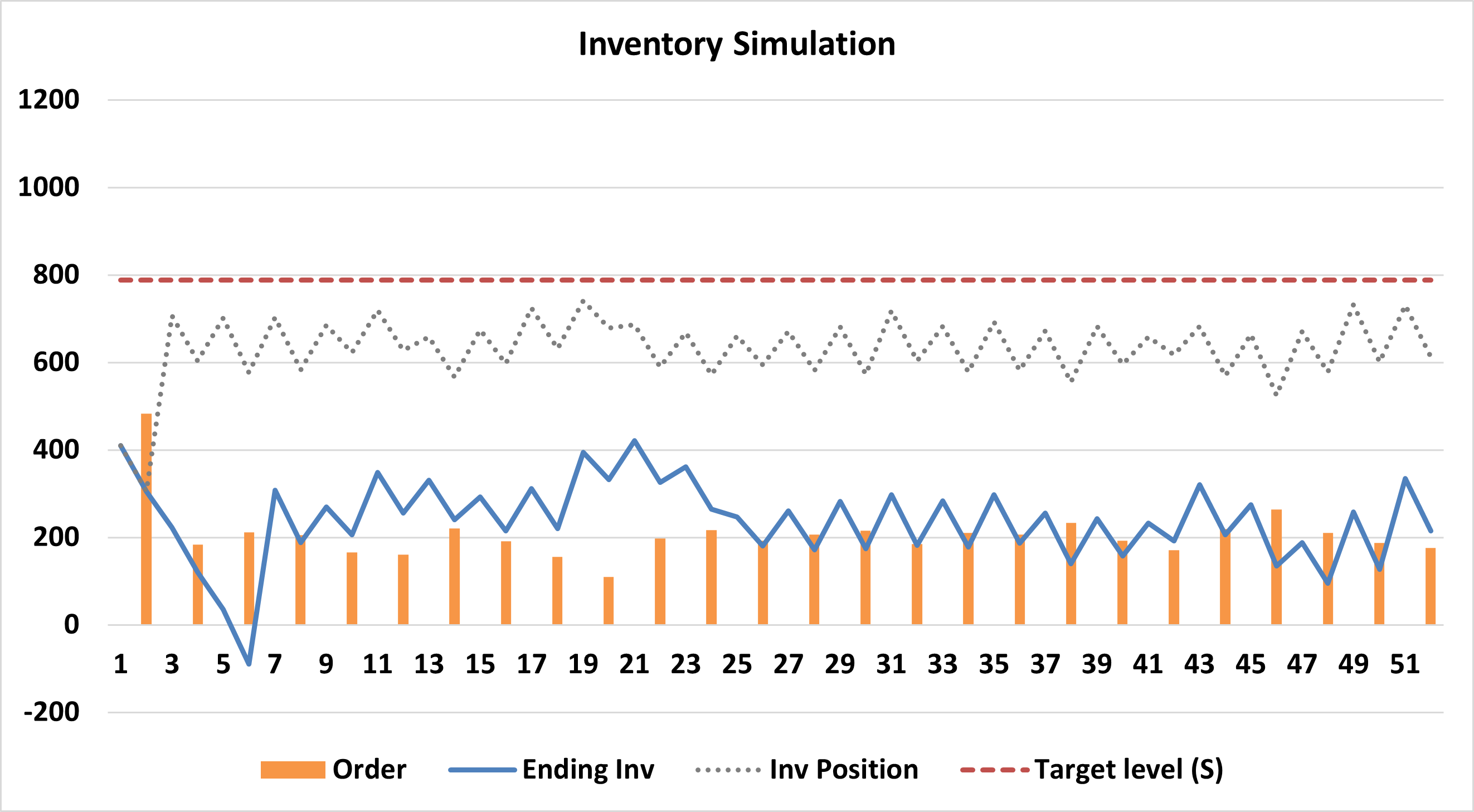
Example for (R,S) policy.
D. The (R, s, S) System (Hybrid)
- Mechanism: Every R units of time, check the inventory:
- If inventory \(\le s\), order up to S.
- If inventory \(> s\), do nothing.
- Best For: A Items (High value/importance).
- Pros: The most “optimal” general form found in mathematical research.
- Cons: Computationally intensive. Finding the best values for all three parameters (R, s, S) requires significant effort.
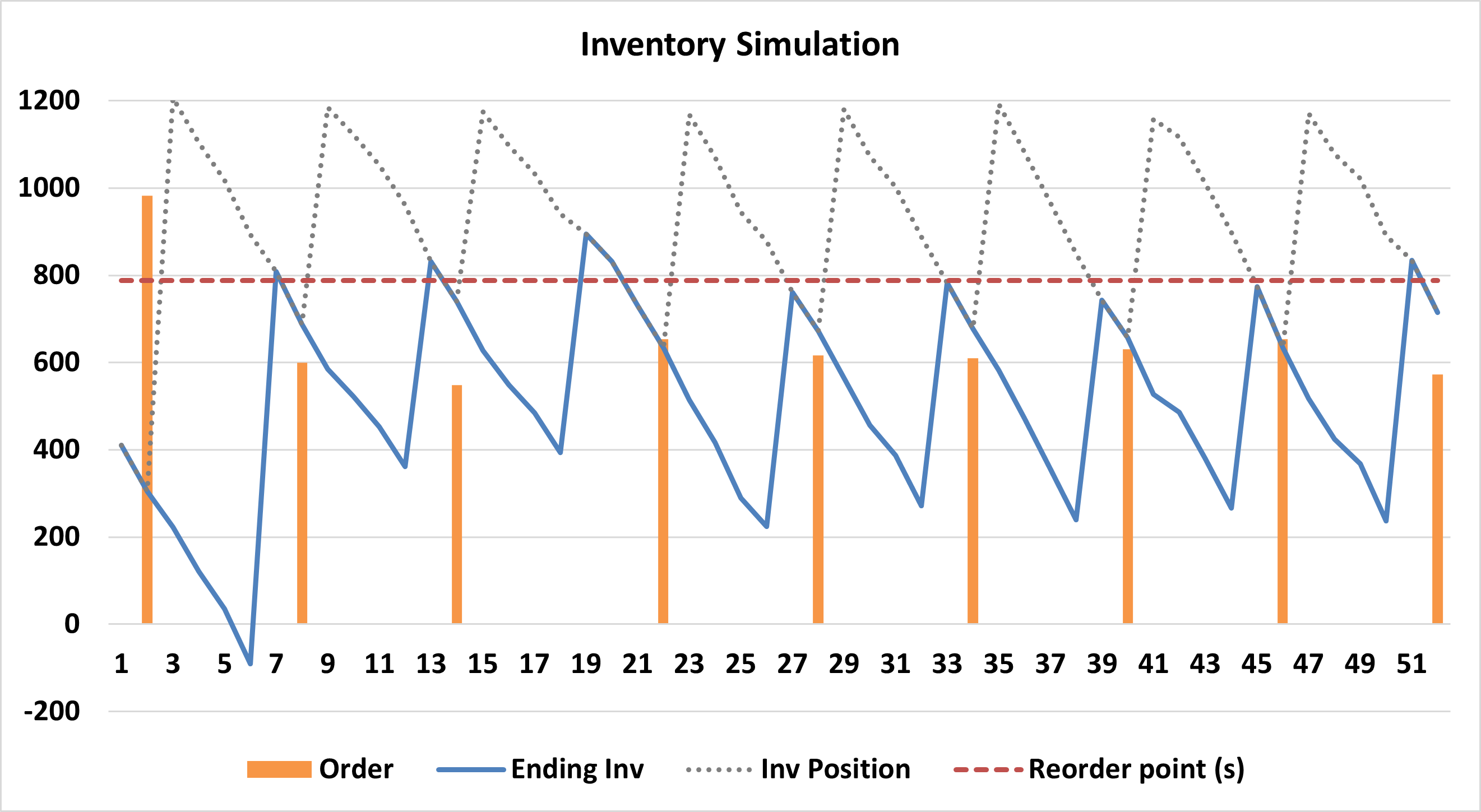
Example for (R,s,S) policy.
(3) Quick Selection Guide
Rules of Thumb for Selecting Policy
| Item Classification | Continuous Review | Periodic Review |
|---|---|---|
| A Items (High Value) | (s, S) | (R, s, S) |
| B Items (Moderate Value) | (s, Q) | (R, S) |